Roof Pitch Calculator
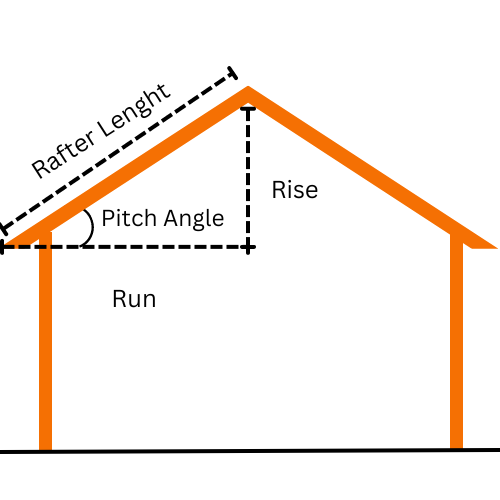
Roof Pitch Visualization
Recommended Roof Rise & Run Chart
| Roof Pitch (Slope) | Rise (ft) | Run (ft) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low slope | 3 ft | 12 ft | Minimal slope, modern homes |
| Moderate slope | 4 – 6 ft | 12 ft | Most common residential roofs |
| Steep slope | 7 – 9 ft | 12 ft | Colonial, snowy regions |
| Very steep | 10 – 12+ ft | 12 ft | Gothic, A-frame cabins |
Roof Pitch Calculator calculates the slope or angle of your roof. Simply input your roof's run and rise values, and the tool will convert the roof pitch into degrees and percentages while also determining the rafter length.
What is Roof Pitch?
Roof pitch refers to the slant or degree of a roof. This is usually a ratio of the pitch of the roof that tells you how much vertical height the roof will rise over a horizontal distance it will cover. For instance, a 4:12 pitch means the roof rises 4 units vertically for every 12 units of horizontal run.
How to Calculate Roof Pitch?
Finding roof pitch is an easy process that only comes down to measuring the angle of your roof. Roof pitch is commonly defined as the ratio of the roof’s vertical rise to its horizontal run, usually abbreviated as “X:12.” A pitch of 4:12, for example, means the roof goes up 4 inches for every 12 inches it runs horizontally.
Here’s how you can measure roof pitch step by step:
- Measure the Run: Place the level horizontally on the roof and make contact with the surface on the end. Mark a point 12 inches at the edge between the level and the roof.
- Take the Rise: From the 12-inch mark, measure vertically up to the surface of the roof. This measurement is the rise for your roof.
- Pitch Calculation: Refer to the longitudinal measurement of the rise and divide by the 12-inch run. For example, if the rise is 6 inches your roof pitch is 6:12.
1. Pitch Ratio Formula
The pitch ratio, also known as the roof pitch or roof slope, describes the steepness of a roof. The pitch ratio is typically written as a fraction (e.g., 1/4, 4/12) or sometimes as a ratio (e.g., 1:4). The first number (numerator) represents the rise, and the second number (denominator) represents the run.
To find the roof pitch ratio you have to divide the rise by the run. This is the most basic formula for roof pitch:
For example, if the rise is 6 inches and the run is 12 inches:
2. Roof Pitch in Degrees
It refers to expressing the steepness of a roof as an angle measured in degrees, rather than as a ratio of rise to run (like 4/12 or 6/12). This angle is formed between the roof surface and a horizontal plane.
To convert the pitch ratio into degrees, use the following formula:
For example, if the rise is 6 inches and the run is 12 inches:
3. Roof Pitch as a Percentage
It is another way to express the steepness of a roof. It represents the ratio of the roof's rise to its run, multiplied by 100 to get a percentage value. Using percentages is just another way to describe the slope of a roof.
To express roof pitch as a percentage:
For example, if the rise is 6 inches and the run is 12 inches:
What Is Rafter Length?
Rafter length is the measurement of the sloping beam (rafter) that spans from the ridge of the roof (the peak) to the edge or eaves of the roof. It is an essential dimension in roof construction, as it determines the size of the rafters needed to support the roof structure effectively.
How to Calculate Rafter Length
Rafter length can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem
Formula for Rafter Length
Example Calculation
If the rise is 6 feet and the run is 12 feet:
Adjusting for Overhang
If the roof has an overhang, you need to add this extra length to the calculated rafter length. For example, if the overhang is 2 feet, the total rafter length will be:
Example with Overhang:
What Is a Roof Pitch Chart?
Roof pitch chart — A roof pitch chart is a reference guide that shows how steep a roof is based on the rise and run ratio. Roof pitch is usually noted as a ratio — 4:12, for example — which means the roof rises 4 inches for every 12 inches of horizontal run. A roof pitch chart summarizes this information and presents it in an easy-to-read format.
Roof Pitch Chart
| Pitch Ratio | Rise (in inches) | Run (in inches) | Angle (in degrees) | Pitch as Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:12 | 1 | 12 | 4.76° | 8.33% |
| 2:12 | 2 | 12 | 9.46° | 16.67% |
| 3:12 | 3 | 12 | 14.04° | 25.00% |
| 4:12 | 4 | 12 | 18.43° | 33.33% |
| 5:12 | 5 | 12 | 22.62° | 41.67% |
| 6:12 | 6 | 12 | 26.57° | 50.00% |
| 7:12 | 7 | 12 | 30.26° | 58.33% |
| 8:12 | 8 | 12 | 33.69° | 66.67% |
| 9:12 | 9 | 12 | 36.87° | 75.00% |
| 10:12 | 10 | 12 | 39.81° | 83.33% |
How to Use a Roof Pitch Chart
- Find the Rise and Run: Measure your roof on the rise and run.
- Locate Your Pitch: Find the pitch ratio that corresponds in the chart (we'll use 6:12 for a 6 inch rise and 12 inch run)
- Read the Data: Figure out the degrees of all pitch angle or pitch percentage with this chart.
How Roof Pitch is Used in Real Life
Knowing roof pitch is important for a few reasons:
- Material Calculator: Calculates the quantity of roofing material needed.
- Why pitch matters: So, more pitch accommodates more drainage speed — that helps to limit leaks and the opportunity for ice dams.
- Building Codes: Minimum roof pitch may be required for safety in certain jurisdictions.
This material can be used for aesthetic design, that is, it influences the look and appearance of the building.
FAQ
What is the angle of a 4/12 pitch roof?
The angle of roof pitch can be calculated angles of a 4/12 pitch roof-The roof angle is based on the slope ratios A 4/12 pitch says that for every 12 horizontal inches, the roof rises 4 inches.
Equation to Determine Roof Pitch:
We can find the roof angle (θ\theta) by applying the arctangent function:
Where:
- = 4 (inches)
- = 12 (inches)
Calculation:
Using a calculator:
Answer:
The angle of a 4/12 pitch roof is approximately 18.43 degrees.
Is it possible to convert a flat roof to a pitched roof?
Yes, a flat roof can be converted into a pitched roof, but the remodeling is extensive. This kind of project is usually done for drainage purposes, aesthetics, or property value increase.
Is there a minimum pitch for a metal roof?
The minimum pitch for a metal roof will vary with the type of metal roofing system that's installed, as well as the manufacturer's recommendations. Generally, the minimum pitch of a roof is:
1. Standing Seam Metal Roof:
- Required Pitch: 1:12 (1 in. of rise for every 12 in. of run)
- Except for mechanically seamed panels engineered for low slopes. For other types of standing seam systems, the minimum is generally 2:12.
2. Corrugated Metal Panels:
- Minimum Pitch: 3:12 (3 inches of rise per 12 inches of run)
- You also need to account for the fact that corrugated panels have overlapping seams that are more susceptible to water infiltration, so the panels must be at a steeper pitch.